NCERT Solutions, Question Answer and Mind Map for Class 10 Social Studies Economics Chapter 3, “Money and Credit,” is a study material package designed to help students understand the concept of money, its role in the economy, and the different sources of credit available in the market.
NCERT Solutions provide detailed explanations and answers to the questions presented in the chapter. The solutions cover all the topics in the chapter, including the functions of money, the evolution of money, the use of credit, and the different sources of credit available in the market. They also provide tips on how to answer different types of questions, including short answer, long answer, and multiple-choice questions.

The question-answer section of the chapter covers a wide range of topics, from the functions of money in an economy to the role of banks and other financial institutions in providing credit to individuals and businesses. It also includes questions on the types of credit available in the market, including formal and informal sources of credit.
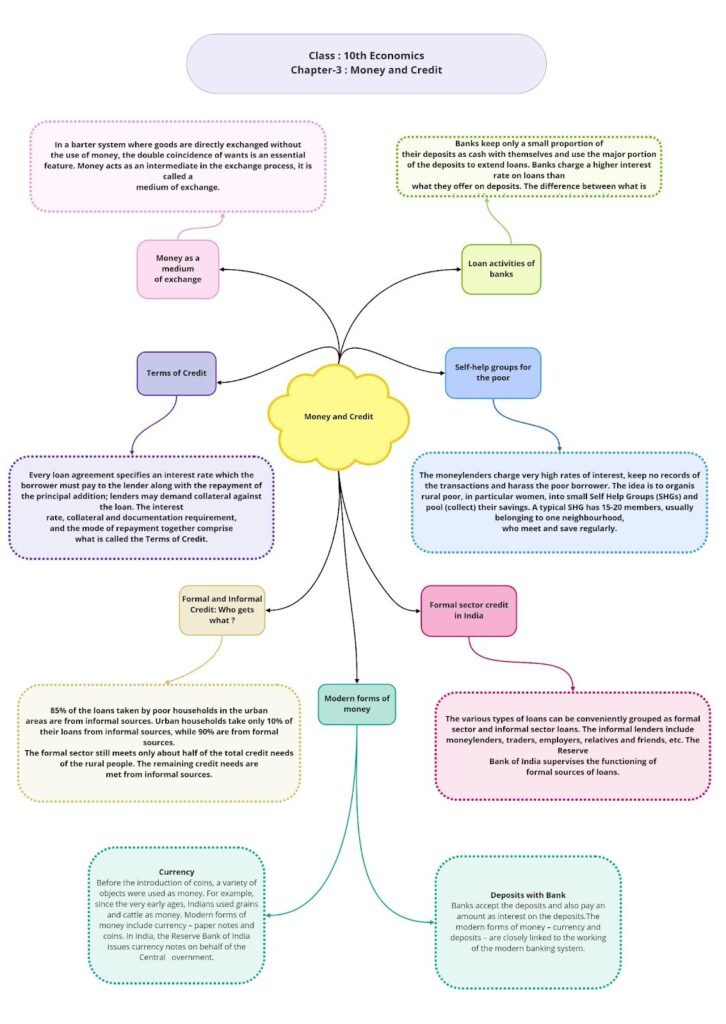
The mind map provides a visual representation of the key topics covered in the chapter, allowing students to understand the connections between different concepts and ideas. The mind map covers the functions of money, the evolution of money, and the sources of credit available in the market.
NCERT Solutions / Notes Class 10 Social Studies Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit with Mind Map PDF Download
Money and Credit
Money as a Medium of Exchange
An intermediary instrument is used to facilitate the sale or purchase of goods between the buyer and the seller. In the olden days, both parties agreed to sell and buy each others’ goods. This is known as the barter system. Here, the double coincidence of wants is an important feature because the goods are directly exchanged without the use of currency. Later, metallic coins of gold, silver and copper were used as a medium of exchange in transaction. In modern economies, money functions as a medium of exchange. A person holding money can exchange it for any desired good and service in the market.

Modern Forms of Money
Modern forms of money are currencies and coins which are authorised by the Government of the country. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issues currency notes on behalf of the Government. The law legalises the use of currency notes as a medium of payment which everyone has to accept in all the transactions in India.
Deposits with Banks
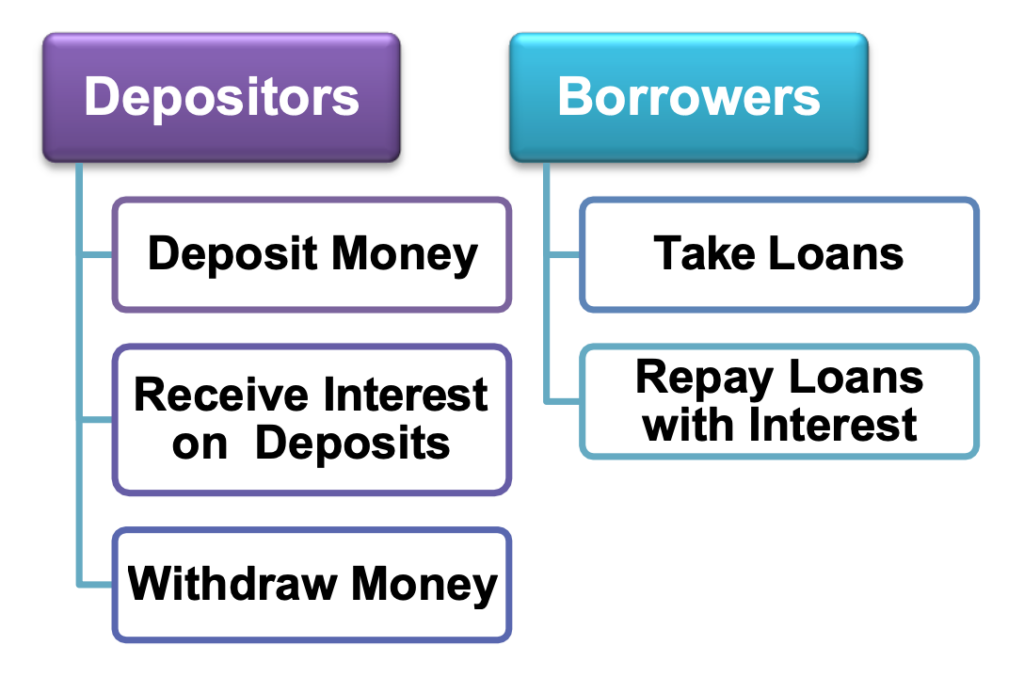
- Cash Deposit: Some people may hold certain amount of money with banks as deposits after meeting the day-to-day expenses. The banker accepts the person’s deposit and pays an amount of interest on the deposits. The deposits in the bank account can be withdrawn on demand, and these deposits are called demand deposits.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
- Cheques: A bank account holder can make payment through a cheque for a specific amount instead of cash. A cheque is a paper with the instruction to the banker to pay the specified amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued.
Bank Loans
The bank maintains only a certain portion of deposits as cash with them and most deposits are used to extend loans. People may require loans for their economic activities. Thus, banks make use of these deposits to meet the loan requirement of people. Banks charge a higher rate of interest on loans than the interest they pay on deposits. The difference between the amount of interest received and paid is their main source of income.
Credits
Credit refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment. Generally, farmers take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest. If the income from the harvest is not sufficient to repay the credit, then a part of the land is sold to repay the credit. This is a situation called debt-trap.
Terms of Credit
- The loan agreement specifies that the borrower needs to pay interest to the lender along with the principal amount, and the lender may demand collateral against loans.
- Collateral is an asset which the borrower owns (such as land, livestock and bank deposits) and uses as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
- Thus, the terms of credit comprise interest rate, collateral, documentation and the mode of repayment.
Loans from Cooperatives
Cooperative societies are the other major source of cheap credit in rural areas. It accepts deposits from farmers and uses it as collateral for obtaining loans from banks. Further, these funds are used to provide loans to members.
Types of Credit in India
Types of loan/credit can be grouped into formal and informal sector loans.
- Loans provided by banks and cooperatives are formal sector loans. The functions of formal sector loans are supervised by RBI. They are
- To maintain minimum cash balance as reserve in the bank.
- To provide loans not only to the profit-making business but also to the small-scale industries, small cultivators and borrowers.
- To submit the periodical report to RBI regarding the total amount extended as credit and the rate of interest charged on credit.
- Loans provided by moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends are informal sector loans. There is no organisation to supervise the activities of the informal sector. These lenders charge a higher rate of interest than banks and cooperatives. Because of the higher interest rate, the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower. Thus, banks and cooperatives need to lend cheap and affordable credit for the country’s development.
Importance of formal and informal sources of credit for people in rural areas:
- Only 50% of the total credit is provided by the formal sector and the remaining by the informal sector.
- The formal sector has to increase the credits in rural areas to reduce the dependence on credits from the informal sector.
- The formal sector loan has to expand and it is equally distributed to everyone.
Self-help Groups for Poor
As the bank requires clear documentation and collateral to avail loans, the poor people depend on informal sources for loans. They are bound to pay high rates of interest for the absence of collateral. Therefore, self-help groups (SHGs) with 15–20 members (particularly women) are formed to pool their savings. A member’s savings may vary from Rs 25 to Rs 100 or above based on their ability to save. Members of the group can take small loans at a reasonable rate of interest. This development of a group helps to obtain loans from banks. Thus, SHGs help borrowers to receive loans without collateral at times of necessity such as for releasing mortgaged land, for meeting working capital needs and for acquiring assets (e.g. sewing machine, handloom and cattle).
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Advantages of Self Help Group (SHG):
- It assists borrowers in overcoming the lack of collateral issues.
- SHGs are the foundations of the rural poor’s organisation.
- People can receive loans on schedule and at a fair interest rate for a number of objectives.
- It assists women in becoming financially self-sufficient.
- The group’s frequent meetings give a forum for discussing and taking action on a variety of social concerns such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, and so on.
Class 10 Social Studies Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions-
Question 1. Farmers usually take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after:
(a) Sowing
(b) Tilling
(c) Harvesting
(d) All the above
Question 2. Credit sometimes, pushes the borrower to a situation from which recovery is:
(а) Easy
(b) Hard
(c) Very painful
(d) None of the above
Question 3. Sometimes lenders demand against loan:
(a) Payment
(b) Cheque
(c) Draft
(d) Collateral
Question 4. Interest rate, security and documentation requirement, and the mode of repayment together comprise what is called the:
(a) Loan factor
(b) Credit factor
(c) Terms of loan
(d) Terms of credit
Question 5. Loans from banks and cooperatives are called:
(a) Mixed loans
(b) Term loans
(c) Formal loans
(d) Informal loan
Question 6. Loans from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends are called:
(а) Mixed loans
(b) Term loans
(c) Formal loans
(d) Informal loans
Question 7. The RBI monitors the banks are actually maintaining:
(а) Cash books
(b) Cash balance
(c) Cash register
(d) None of the above
Question 8. Most of the informal lenders charge:
(a) A less interest on loans
(b) A much higher interest on loans
(c) Can be both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Question 9. The rich households are availing cheap credit from formal lenders whereas the poor households:
(a) Do not get a loan
(b) Get loan at a much less interest
(c) Have to pay a heavy price for borrowing
(d) None of the above
Question 10. Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for:
(а) The development of urban areas
(b) The development of rural areas
(c) The country’s development
(d) All the above
Question 11. About 85 percent of the loans taken by poor households in the urban areas are from:
(a) Formal sources
(b) Informal sources
(c) Mixed sources
(d) None of the above
Question 12. Most loans from informal lenders carry a very high interest rate and do little to:
(a) Do anything for the poor
(b) Pay the loans
(c) Increase the income of the borrowers
(d) None of the above
Question 13. It is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that:
(a) The rich can benefit from the cheaper loans
(b) The poor can benefit from the cheaper loans
(c) The women can benefit from the cheaper loans
(d) None of the above
Question 14. The full form of SHG is:
(а) Station House Guard
(b) State Housing Guarantee
(c) Self Happy Groups
(d) Self Help Groups
Question 15. The SHGs help borrowers overcome the problem of:
(а) Lack of funds
(b) Lack of money
(c) Lack of collateral
(d) None of the above
Very Short Questions-
Question 1. The currency notes on behalf of the Central Government are issued by whom? (2011 D)
Question 2. Why do banks ask for collateral while giving credit to a borrower? (2014 D, 2011 OD)
Question 3. What do banks do with the deposits they accept from customers? (2012 D)
Question 4. What comprises ‘terms of credit’? (2012 OD)
Question 5. What is the main informal source of credit for rural households in India? (2013 D)
Question 6. Which body supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans? (2013 OD)
Question 7. ‘Modern currency is without any use of its own’; then why is it accepted as a medium of exchange? (2014 OD)
Question 8. What is the meaning of ‘barter system’? (2015 D)
Question 9. What is the meaning of ‘investment’? (2015 D)
Question 10. What is meant by double coincidence of wants? (2015 OD)
Short Questions-
Question 1. What is money? Why is modern money currency accepted as a medium of exchange? (2012 D)
Question 2. What are the modern forms of money? Why is the ‘rupee’ widely accepted as a medium of exchange? Explain two reasons. (2013 D)
Or
Why is modern currency accepted as a medium of exchange without any use of its own? Give reasons?
Question 3. What is collateral? Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending? Explain. (2012)
Question 4. “Cheap and affordable credit is essential for poor households both in rural and urban areas.” In the light of the above statement explain the social and economic values attached to it. (2013 OD)
Or
“Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development.” Assess the statement. (2016 D)
Or
‘Credit has its own unique role for development’. Justify the statement with arguments. (2016 OD)
Question 5. How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants? Explain with an example. (2014 D)
Question 6. How is money used in everyday life? Explain with examples. (2014 D)
Question 7. Explain with examples, how people are involved with the banks. (2014 D)
Question 8. Why is it necessary for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas? Explain. (2015 D)
Question 9. How can money be easily exchanged for goods or services? Give an example to explain. (2016 D)
Question 10. “The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.” Support the statement with arguments. (2016 D)
Long Questions-
Question 1. What is the basic objective of ‘Self Help Groups’? How do they work? Describe any four advantages of ‘Self Help Groups’ for the poor. (2015 D, 2011 D)
Question 2. ‘Banks and cooperatives help people in obtaining cheap and affordable loans’ Which values according to you does this support? (2011 OD)
Question 3. What is Credit? Why is cheap and affordable credit important for the country’s development? Give four reasons. (2012 D)
Or
What is credit? Explain with an example, how credit plays a vital and positive role for development. (2014 OD)
Question 4. What are the two categories of sources of credit? Mention four features of each. (2013 OD)
Question 5. Which government body supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans in India? Explain its functioning. (2012 OD)
Question 6. What are the various sources of credit in rural areas? Which one of them is the most dominant source of credit and why? (2013 D)
Question 7. “Deposits with the banks are beneficial to the depositors as well as to the nation”. Examine the statement. (2016 OD, 2015 D)
Question 8. How do banks play an important role in the economy of India? Explain. (2015 OD)
Assertion Reason Questions:
- Directions: – In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of
assertion. - Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion. - Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Assertion (A): Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, deposits with banks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
Reason (R): Collateral is given as the lender can sell the collateral to recover the loan
amount if the borrower fails to repay the loan.
- Directions: – In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
- Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of
assertion. - Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion. - Assertion is true, but reason is false.
- Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion (A): Banks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits.
Reason (R): The difference between what is charged from borrowers and what is paid to
depositors is their main source of income.
Case Study Questions:
- Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Swapna, a small farmer, grows groundnut on her three acres of land. She takes a loan from the moneylender to meet the expenses of cultivation, hoping that her harvest would help repay the loan. Midway through the season, the crop is hit by pests and the crop fails. Though Swapna sprays her crops with expensive pesticides, it makes little difference. She is unable to repay the moneylender, and the debt grows over the year into a large amount. Next year, Swapna takes a fresh loan for cultivation. It is a normal crop this year. But the earnings are not enough to cover the old loan. She is caught in debt. She has to sell a part of the land to pay off the debt.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option
- The passage given above relates to which of the following options:
- Collateral Credit.
- Credit recovery is very painful.
- Failure of Crops.
- Credit is somewhere beneficial.
- According to the passage, Swapna faced which of the following options:
- The crop is hit by pests and the crop fails.
- She had to sell a part of the land to pay off the debt.
- Credit left her worse off.
- All of these.
- It refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment:
- Terms and Credit.
- Credit.
- Depositor.
- Borrower.
- The above passage is an example of:
- Collateral.
- Debt Trap.
- Credit plays a vital and positive role.
- None of these.
- Read the source given below and answer the following questions:
Getting a loan from bank is much more difficult than taking loan from informal sources. Absence of collateral security and documentation prevents the poor’s from getting bank loans. Self Help Group is a group of people usually belonging to one neighbourhood having same social and economic backgrounds. They meet and save money regularly as per their ability. Members of the group can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs. The group charges interest less than moneylenders on these loans. After one or two years, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank. Loan is sanctioned in the name of group and is meant to create self-employment opportunities.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
- What is the most essential requirement for taking loan from information services?
- Collateral security.
- Bribe.
- Source from a top officer.
- None of these.
- SH G is a group of people usually belonging to:
- The same caste.
- Nearby villages.
- One neighbourhood having same social and economic backgrounds.
- Different villages.
- What facilities do the members have who are in the same group?
- They are not given any facility.
- They can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs.
- They are debarred from the group.
- No facility is given to them.
- What benefits are there for a SHG that is regular in savings?
- The dispute arise after sometimes.
- They are rewarded by the government.
- They get jobs in government departments.
- They are entitled to raise loan from bank in the name of SHG.
MCQ Answers-
- Answer: (c) Harvesting
- Answer: (c) Very painful
- Answer: (d) Collateral
- Answer: (d) Terms of credit
- Answer: (c) Formal loans
- Answer: (d) Informal loans
- Answer: (b) Cash balance
- Answer: (b) A much higher interest on loans
- Answer: (c) Have to pay a heavy price for borrowing
- Answer: (c) The country’s development
- Answer: (b) Informal sources
- Answer: (c) Increase the income of the borrowers
- Answer: (b) The poor can benefit from the cheaper loans
- Answer: (d) Self Help Groups
- Answer: (c) Lack of collateral
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Very Short Answers-
- Answer: Reserve Bank of India.
- Answer: Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (land, building, vehicle, livestock, land documents, deposits with banks, etc.) which stands as a security against the money borrowed. In case the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral.
- Answer: Banks use a major portion of deposits to extend loans to people.
- Answer: Interest rate, collateral and documentation requirement and mode of repayment together comprise terms of credit.
- Answer: Money lenders are the main source of informal credit for rural households.
- Answer: Reserve Bank of India.
- Answer: Modern currency is accepted as a medium of exchange because it is certified for a particular denomination (?10, ?100, etc.) of the country by authorities set up by the Central Government. It is issued by the Reserve Bank of India and it can be used for buying any commodity which is on sale. It is authorized by the government of the country.
- Answer: Barter system refers to the system of exchange of goods and services. It is the system by which one commodity is exchanged for another without the use of money. Before money was introduced, people practiced barter system.
Example: A farmer could buy a dhoti from a weaver or a pair of shoes from a cobbler in exchange of grains he produced.
- Answer: Investment is buying of an asset in the form of a factory, a machine, land and building, etc. (physical assets) or shares (monetary assets) for the purpose of making or sharing profits of the enterprises concerned.
Common investments are—buying land, factories, machines for faster production, buying small local companies to expand production, cheap labour, skilled engineers, IT personnel, etc.
- Answer: Double coincidence of wants means when both parties have agreed to sell and buy each other’s commodities.
Short Answers-
Answer 1: Money is a medium of exchange in transactions. A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want.
Modem money currency is accepted as a medium of exchange because
- it is certified for a particular denomination (For example, ₹ 10, ₹ 20, ₹ 100, ₹ 1,000).
- it is issued by the Central Bank of the country.
- it is authorized by the government of the country.
Answer 2: Modem forms of money currency in India include paper notes and coins which are known as Rupees and Paise.
- It is accepted as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorized by the Government of India.
- In India, the Reserve bank of India issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government of India.
- The law legalizes the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in settling transaction in India.
- No Individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees.
Therefore, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
Answer 3: Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (land, building, vehicle, livestock, land documents, deposits with banks etc.) which stands as a security against the money borrowed. In case the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to recover the loan money. Most lenders ask for collateral while lending as a security against their own funds.
Answer 4: Credit means loAnswer: It refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future repayment.
- Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s growth and economic development. Credit is in great demand for various kinds of economic activities—big or small investments, to set up business, buying cars, houses, etc.
- In rural areas credit helps in the development of agriculture by providing funds to farmers to buy seeds, fertilizers, expensive pesticides.
- Manufacturers need credit for buying raw material or to meet ongoing expenditure of production. Credit helps in the purchase of plant, machinery, equipment, etc.
- Some people may need to borrow for illness, marriages etc.
Thus, cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s growth and economic development.
Answer 5: Money acts as a medium of exchange. Money can be exchanged for any kind of commodity or service of one’s choice or need. Before money was introduced, people practised barter system. They exchanged goods with each other.
Example, A farmer could buy a dhoti from a weaver or a pair of shoes from a cobbler in exchange of grains he produced.
The problem with the barter system was that both the parties had to agree to sell and buy each other’s product. This is known as double coincidence of wants.
In barter system, where goods are directly exchanged without the use of money, it is essential that there is a double coincidence. Double coincidence is a situation where two persons need or desire to have each other’s product.
Money solves this problem as with money we can buy whatever we want and whenever we want, without having to exchange something in return.
Answer 6:
- Money plays a central role in our daily life. It is used as a medium of exchange to carry out transactions.
- Money buys us food, clothing, shelter and other basic necessities of life.
- Money provides us social security. It is needed to procure services like transport, education, healthcare, entertainment, recreation, and so on. Money facilitates business and trade and is the basis of the working of an economy.
Answer 7:
- Banks help people to save their money and keep their money in safe custody of the bank. Banks accept deposits from the public and also help people to earn interest on their deposits.
- People can withdraw the money deposited with the bank at the time of their need. As the money can be withdrawn on demand, these are called demand deposits.
- Banks also grant loans to people for a variety of purposes. In times of need individuals, business houses and industries can borrow money from the banks.
Answer 8: Banks and Cooperatives can help people in obtaining cheap and affordable loans. This will help people to grow crops, do business, set up small-scale industries or trade in goods and also help indirectly in the country’s development. They should do so, so that relatively poor people do not have to depend on informal sources of credit (money-lenders).
Answer 9: Money as a medium of exchange for goods and services:
A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want. Everyone prefers to receive payments in money and exchange the money for things they want.
For example: A shoemaker wants to sell shoes in the market and buy wheat. The shoe maker will first exchange shoes for money and then exchange the money for wheat. If the shoemaker had to directly exchange shoes for wheat without the use of money, he would have to look for a wheat growing farmer who not only wants to sell wheat but also wants to buy the shoes in exchange. Both the parties have to agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities. This process is very difficult, time consuming and unhealthy.
Answer 10: The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged because:
- 85% of loans taken by the poor households in the urban areas are from informal sources. There is no organisation that supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector.
- Informal lenders charge very high interest on their loAnswer: They try to charge more and more interest on their loans as there are no boundaries and restrictions.
- Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
- In certain cases, the high interest rate for borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of borrower. This could lead to increasing debt and debt trap, therefore the credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Long Answers-
Answer 1: The basic objective of ‘Self Help Groups’ is to organize rural poor, particularly women belonging to one neighbourhood into small Self Help Groups (15-20 members). These members save regularly and the amount varies from ₹25-100 or more depending upon their ability to save.
The four advantages of ‘Self Help Groups’ are as follows:
- The members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs. The group charges interest on these loans which is still less than what moneylenders charge.
- After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank which is sanctioned in the name of the group to create self employment opportunities. All important decisions regarding loan, purpose, amount of interest, non-payment of loan are taken by the group members.
For instance, small loans are provided to the members for releasing mortgaged land, meeting working capital needs, for acquiring assets like sewing machines, handlooms, cattle etc.
- Since non-repayment of loans is dealt with seriously by group members, therefore banks are willing to lend to the poor women when organized in SHGs, even though they have no collateral as such. Thus, the SHGs help women to become financially self reliant.
- The regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence etc.
Answer 2: Cheap and affordable loans help people to grow crops, do business, set up small scale industries or trade in goods.
This promotes:
- Self reliance and financial security and independence of people.
- Protection of the relatively poor against corrupt moneylenders.
- Eradication of poverty in general.
- All this indirectly helps in the country’s development.
Answer 3: Credit means loans. It refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future repayment.
- Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s growth and economic development. Credit is in great demand for various kinds of economic activities—big or small investments, to set up business, buying cars, houses, etc.
- In rural areas credit helps in the development of agriculture by providing funds to farmers to buy seeds, fertilizers, expensive pesticides.
- Manufacturers need credit for buying raw material or to meet ongoing expenditure of production. Credit helps in the purchase of plant, machinery, equipment, etc.
- Some people may need to borrow for illness, marriages etc.
Thus, cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s growth and economic development.
Answer 4: The two sources of credit are formal sources and informal sources:
Formal sources of credit:
- Banks and cooperative societies fall under the formal sector. One can obtain loans from banks or cooperative societies.
- The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loAnswer:
- Bank loans require documentation and collateral (collateral is an asset such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, deposits with the bank, etc.). This is used as a guarantee to the lender until the loan is paid back.
- Formal sources cannot charge any rate of interest from the borrowers according to their whims.
Informal sources of credit:
- In the informal sector money can be borrowed from a person, friend, relative, moneylender, traders, employers, etc.
- There is no organization that checks or supervises the activities of lenders in the informal sector.
- Loans from informal sources do not require any such collateral.
- They charge a very high rate of interest on loans as they do not require any collateral.
Answer 5: The Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sources of loans.
Functions of Reserve Bank of India.
- RBI requires commercial banks to maintain a minimum cash balance out of the deposits they receive. The RBI monitors that the banks actually maintain the cash balance.
- RBI sees that the banks give loans not just to profit-making businesses and traders but also to small cultivators, small-scale industries, small borrowers, SHGs, etc.
- RBI issues guidelines for fixing rate of interest on deposits and lending by commercial banks.
- Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom, at what interest rate, etc.
Answer 6: Moneylenders are the most dominant amongst sources of credit for rural households. They constitute an informal source of credit. They charge a very high rate of interest on loans as they do not require any collateral. They are the most convenient source of credit in the rural areas.
Other sources of rural credit:
- Cooperative Societies are another major source of rural credit. They are a source of formal sector credit. Members of a Cooperative pool their resources for helping one another, e.g., Farmers’ Cooperatives, Weavers’ Cooperatives, etc. They offer cheap credit in rural areas for their members. Once these loans are repaid, another round of loans is offered.
- Agricultural traders, relatives and friends are other informal sources of rural credit. Some farmers borrow from agricultural traders who supply the farm inputs (such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, etc.) on credit at the beginning of the cropping season and repay the loans after the harvest.
- Commercial banks also give loans to rural households. However, not many rural households borrow from banks as they require proper documentation and collateral.
Answer 7: Benefit of deposits to the depositors:
- Bank accepts the deposits and pays interest to the depositor.
- Banks help people save their money and keep their money in safe custody of the bank.
- People can withdraw the money as and when they require.
- Banks also grant loans to people for a variety of purposes. In times of need, individuals, business houses and industries can borrow money from the banks.
Benefit of deposits to the Nation:
- Banks use the major proportion of the deposit to extend loans.
- There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities. In times of need, business houses and industries can borrow money from the banks.
- Banks mediate between those who have surplus funds and those who are in need of these funds. Thus, it helps in the economic development of the Nation.
Answer 8:
- Banks help people to save their money and keep their money in safe custody. To ensure safety of their money, people deposit their money with banks. Banks accept deposits and pay interest on deposits. People have the provision to withdraw their money as and when they require.
- Banks also grant loans to people for a variety of purposes. In times of need individuals, business houses and industries can borrow money from the banks.
- Credit provided by banks is crucial for the country’s growth and economic development. Credit is needed for all kinds of economic activities, to set up business, buy cars, houses, etc.
- Banks also help people in obtaining cheap and affordable loans. This can help people to grow crops, do business, set up small-scale industries or trade in goods and also help indirectly in the country’s development. They should do so, so that relatively poor people do not have to depend on informal sources of credit (money-lenders).
Assertion Reason Answer:
- (a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- (a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Case Study Answer:
| (i) | (a) | Collateral Credit. |
| (ii) | (d) | All of these. |
| (iii) | (a) | Terms and Credit. |
| (iv) | (b) | Debt Trap. |
| (i) | (a) | Collateral security. |
| (ii) | (c) | One neighbourhood having same social and economic backgrounds. |
| (iii) | (b) | They can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs. |
| (iv) | (d) | They are entitled to raise loan from bank in the name of SHG. |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science History: India and the Contemporary World-II
| Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| Chapter 3 The Making of Global World |
| Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation |
| Chapter 5 Print Culture and the Modern World |
