NCERT Solutions, Question Answer and Mind Map for Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 7, “Outcomes of Democracy,” is a study material package designed to help students understand the outcomes and benefits of a democratic system of government.
NCERT Solutions provide detailed explanations and answers to the questions presented in the chapter. The solutions cover all the topics in the chapter, including the meaning and significance of democracy, the importance of free and fair elections, the role of citizens in a democracy, and the need for transparency and accountability in governance. They also provide tips on how to answer different types of questions, including short answer, long answer, and multiple-choice questions.

The question-answer section of the chapter covers a wide range of topics, from the advantages of a democratic system of government to the challenges and limitations of democracy. It also includes questions on the role of media and civil society organizations in promoting democracy and ensuring accountability.
The mind map provides a visual representation of the key topics covered in the chapter, allowing students to understand the connections between different concepts and ideas. The mind map covers the various outcomes of a democratic system of government, such as political equality, social justice, and economic growth.
NCERT Solutions / Notes Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy with Mind Map PDF Download
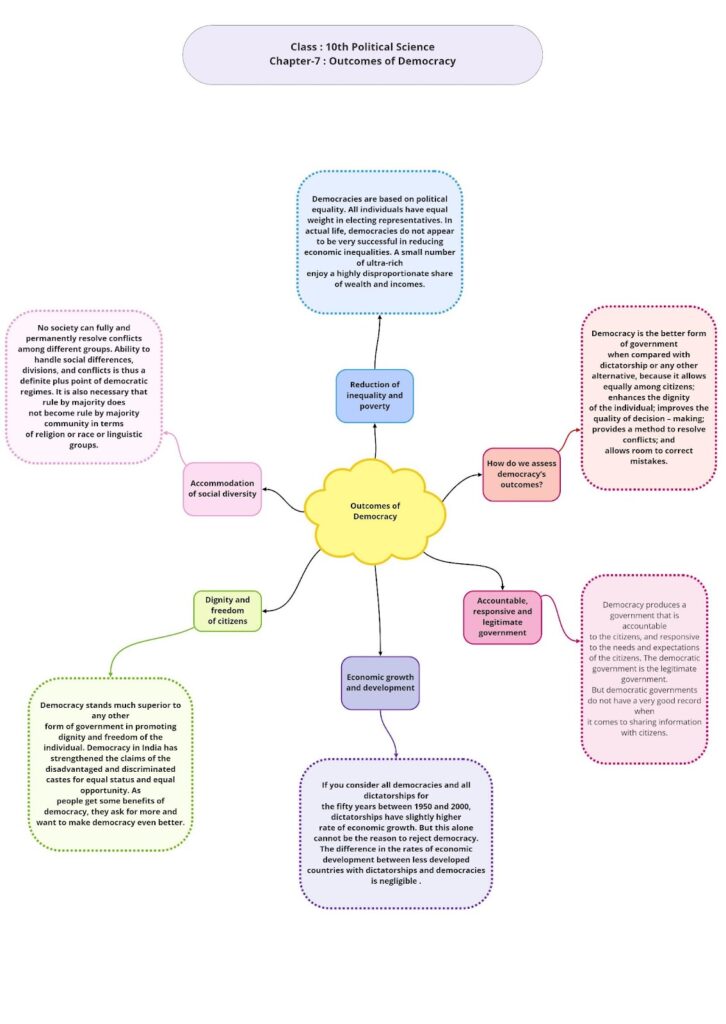
Outcomes of Democracy
Democracy
A democratic or an elected form of government is better than any other form of government. This is because a democratic government ensures
- Equality among citizens
- Dignity of every individual
- Improvement in the quality of decision making
- Several alternatives to resolve conflicts
- Correction of mistakes made previously
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Many people argue against following a democratic form of government. However, it has to be remembered that one democratic country may be different from the other. Further, democracy is just a form of government where the citizens have to take an advantage of the existing conditions. Democracy cannot achieve economic and political equality without the cooperation of the citizens.
Outcomes of a Democratic Government
Results and outcomes of a democracy:
- A democratic government is accountable to the citizens and responsible for the needs and aspirations of the countrymen.
- It is an efficient government. A democratic government may take time to arrive at certain laws and agreements because it has to look after the needs of every section of society. Laws are implemented after deliberations and negotiations which are accepted by people at large unlike a dictatorial government which enacts laws without bothering about its people.
- In a democratic government, the working of the government machinery is transparent. It means a citizen can enquire if any decision was taken based on prescribed norms and procedures. Thus, a democratic government follows procedures and is accountable to the people.

- In most democratic countries, free and fair elections are held regularly. However, many countries still experience rigging of elections which is the biggest challenge which a democratic country faces.
- Although a democratic government may be slow in forming laws, implementing reforms and less efficient on certain occasions, it is the legitimate form of government which is formed by the people themselves.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Democracy and Economic Growth
If democracy produces good governance, then should we not expect the government to also ensure development? According to a survey, dictatorial countries have shown a slightly higher rate of development in the last fifty years.
However, this factor alone cannot undermine the importance of a democratic country because of the following reasons:
- Economic development depends on certain factors such as the population of the country, availability of natural resources, economic trade policies and global cooperation.
- Dictatorial regimes have a little better record in economic terms only in developing countries. In poor countries, there is hardly any economic growth.
- In many democratic countries, unsatisfactory growth rates can be attributed more to inequalities of income in society. Further, there is inequality of opportunity in the poorer sections of society.
We can conclude that though democracy is the best form of government, it has not been able to reduce economic inequalities in society. Sometimes, even a government elected mostly by the poor people does not resolve the issue of poverty in the country. For example, in Bangladesh, more than 50% of its population lives below the poverty line, still the government has failed to work for the upliftment of its people.

Accommodation of Social Diversity
A democratic country looks into the needs and aspirations of every section of society. It is also able to handle social conflicts, divisions and differences. However, in order to achieve this objective, a democratic government should fulfil the following conditions:
- In a democratic government, the majority should work in close cooperation with the minority.
- The rule of the majority community should not be taken in the religious or linguistic sense alone. The rule of a majority should apply in every decision taken and in the formulation of economic policies. Thus, every citizen should get an opportunity to become a part of the majority at some point of time.
We can thus conclude that democracy is the best form of government in the sense that it is elected by the people and it promotes dignity and freedom of an individual. In India, the Constitution does not allow discrimination among people on the basis of religion, caste, gender or sect. A democratic government transforms people from subjects to free citizens.
Dignity and Freedom of the Citizens
Democracy stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting the dignity and freedom of the individual. The passion for respect and freedom are the basis of democracy. Let’s take the case of the dignity of women. The long struggles by women have created some sensitivity that respect and equal treatment of women are necessary ingredients of a democratic society. The same is true of caste inequalities. Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for equal status and equal opportunity.
Most individuals today believe that their vote makes a difference to the way the government is run and to their own self-interest. Democratic examination never gets over. As it passes one test, it produces another test. As people get some benefits of democracy, they ask for more and want to make democracy even better. The fact that people are complaining is itself a testimony to the success of democracy.
Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 7 Outcomes of Democracy Important Questions
Multiple Choice questions-
Question 1. The difference in the rates of economic developments between less developed countries with dictatorships and democracies is:
(a) Less
(b) More
(c) Negligible
(d) None of the above
Question 2. Democracies are based on:
(а) Social equality
(b) Caste equality
(c) Economic equality
(d) Political equality
Question 3. Democracies do not appear to be very successful in:
(а) Reducing economic inequalities
(b) Reducing political inequalities
(c) Reducing caste distinction
(d) All the above
Question 4. The poor constitute:
(а) A small proportion of our voters
(b) A large proportion of our voters
(c) Less amount of money
(d) None of the above
Question 5. People in several poor countries are now dependent on the rich countries:
(a) For education
(b) For weapons
(c) Food supplies
(d) For medicines
Question 6. Democracies usually develops a procedure to:
(a) Fulfil their needs
(b) Give equal rights to all
(c) Conduct their competition
(d) None of the above
Question 7. No society can fully and permanently resolve conflicts:
(a) Among caste systems
(b) Rich and poor
(c) Among different groups
(d) None of the above
Question 8. Non-democratic regimes often turn a blind eye to:
(а) Caste differences
(b) Religious differences
(c) Social differences
(d) None of the above
Question 9. Majority and minority opinions are:
(a) Permanent
(b) Not permanent
(c) Temporary
(d) None of the above
Question 10. Democracy remains democracy only as long as every citizen has a chance of being:
(a) Minority at some point of time
(b) Majority at some point of time
(c) Fully recognized
(d) None of the above
Question 11. Democracy stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting:
(а) Dignity and freedom of the individual
(b) Freedom of the people
(c) Rights of people
(d) None of the above
Question 12. Most societies across the world were historically:
(a) Male dominated societies
(b) Female dominated societies
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) All the above
Question 13. Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for:
(а) Their upliftment
(b) For equal status
(c) For equal status and equal opportunity
(d) All the above
Question 14. The most distinctive feature of democracy is that:
(a) It is the right government
(b) It considers rich and poor equal
(c) Its examinations never gets over
(d) None of the above
Question 15. Most individuals today believe that their vote makes a difference to the way the government:
(а) Is run and to their own self-interest
(b) Can be changed
(c) Can be destroyed
(d) None of the above
Very Short Questions-
1. Name the law which empowers the people to find out what is happening in government?
2. Give one characteristics of democracy.
3. When was democracy introduced in India?
4. What is the basic element of democracy?
5. Mention the terms in which democracies are different from one another.
6. Mention the way in which the democratic government a transparent government.
7. Who are the real rulers in democracy?
8. In which area does the democracy fails to achieve in contrary to other forms of government?
9. What do you understand by outcomes of democracy?
10. Write any two basic element of democracy.
Short Questions-
1. List the various aspects and qualifications which help in giving a clear definition of democracy.
2. “Democratic governments are better than its alternatives”. Explain the statement?
3. How democracy accommodates social diversity?
4. How can we measure democracy on the basis of its expected outcome?
5. What is meant by an accountable, responsive and legitimate government? Explain.
6. “Any imperfection in the government functions is blamed on democracy”. Is it right?
7. Why we felt that democracy is a better form of Government? Give reasons
8. What outcomes can one reasonably expect of democracy?
9. Are democracies based on political and economic equalities? Explain.
10. How is democratic government known as responsive government? Explain.
Long Questions-
1. Democracy means delay in the decision making. Which one is preferable-quick decision making process of dictatorship or slow decision making process of democracy?
2. How can democracy accommodate the dignity of women and caste discrimination in one system?
3. Democracies lead to peaceful and harmonious life among citizens.” Support this statement with suitable arguments.
4. Do you believe that democracy can reduce economic disparities? Give reasons to support your answer.
5. “Corruption is a serious problem faced the Indian Democratic System”. Explain.
6. How do people take part in decision making in democracy? Explain.
7. Which factors sustain democracy in India?
8. How do we assess democracy’s outcome?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Assertion Reason Questions:
- Directions: – In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is correct but R is wrong.
- A is wrong but R is correct.
Assertion (A): Most societies across the world were historically male dominated
societies.
Reason(R): Equal treatment of women is not a necessary ingredient of a democratic
society
- Directions: – In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- A is correct but R is wrong.
- A is wrong but R is correct.
Assertion (A): Democracies do not appear to be very successful in reducing economic inequalities.
Reason(R): The majority of Indian Voters are poor.
Case Study Questions:
- Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
In a democracy, we are most concerned with ensuring that people will have the right to choose their rulers and people will have control over the rulers. Whenever possible and necessary, citizens should be able to participate in decision making, that affects them all. Therefore, the most basic outcome of democracy should be that it produces a government that is accountable to the citizens, and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens. Some people think that democracy produces less effective government. It is, of course, true that nondemocratic rulers are very quick and efficient in decision making and implementation, whereas democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation. So, some delay is bound to take place. But, because it has followed procedures, its decisions maybe both more acceptable to the people and more effective. Moreover, when citizens want to know if a decision was taken through the correct procedures, they can find this out. They have the right and the means to examine the process of decision making. This is known as transparency. This factor is often missing from a non-democratic government. There is another aspect in which democratic government is certainly better than its alternatives: democratic government is legitimate government. It may be slow, less efficient, not always very responsive, or clean. But a democratic government is people’s own government.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
- People’s right to choose their own rulers is called as the:
- Right to Initiate.
- Right to Plebiscite.
- Right to Vote.
- Right to Referendum.
- Which of the following options helps in promoting transparency in the governance?
- Right to education.
- Right to information.
- Right against exploitation.
- Right to speech and expression.
- __________ make/ s the government legitimate.
- Credibility of politicians.
- People’s movements.
- Free and fair elections.
- Holding of powers.
- Decisions in a democracy are more acceptable to the people because they are:
- Taken swiftly and implemented quickly.
- Taken by giving privileges to the people.
- Taken through elites’ votes.
- Taken after following due processes.
- Read the given extract and answer the following questions.
Democracies are based on political equality. All individuals have equal weight in electing representatives. Parallel to the process of bringing individuals into the political arena on an equal footing, we find growing economic inequalities. A small number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly disproportionate share of wealth and incomes. Not only that, their share in the total income of the country has been increasing. Those at the bottom of the society have very little to depend upon. Their incomes have been declining. Sometimes they find it difficult to meet their basic needs of life, such as food, clothing, house, education, and health.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
- Democracies are based on which type of equality?
- Political equality.
- Social equality.
- Economic equality.
- Religious equality.
- Why all individuals have equal weight in electing representatives?
- There is political equality for all individuals.
- Equal opportunities.
- Equal protection of law.
- None of these.
- What are the basic needs of life?
- Wealth.
- Food, clothing, house, education and health.
- Property.
- Foreign Trip.
- Why those at the bottom of the society, have very little resources?
- Their income is very less.
- They are educated.
- They are extravagant.
- None of these.
MCQ Answers-
- Answer: (c) Negligible
- Answer: (d) Political equality
- Answer: (а) Reducing
- Answer: (b) A large proportion of our voters
- Answer: (c) Food supplies
- Answer: (c) Conduct their competition
- Answer: (c) Among different groups
- Answer: (c) Social differences
- Answer: (b) Not permanent
- Answer: (b) Majority at some point of time
- Answer: (а) Dignity and freedom of the individual
- Answer: (a) Male dominated societies
- Answer: (c) For equal status
- Answer: (c) Its examinations never gets over
- Answer: (а) Is run and to their own self-interest
Very Short Answers-
- Ans. Right to information Act
- Ans. .Democracies have greater success in setting up regular and free elections
- Ans. 1950
- Ans. Universal adult franchise
- Ans. .Democracies are different in terms of Culture, social situation and economic activities.
- Ans. It provides to its citizens a right and means to examine the process of decision-making. Example: Right to information Act.
- Ans. The Voters
- Ans. Democracy fails to achieve higher economic development.
- Ans. It means results, consequences, and outputs of democracy are known as outcomes of democracy.
- Ans. Liberty and Equality
Short Answers-
1. Ans.
1. The rulers elected by the people must take all the major decisions
2. Elections must offer a choice and fair opportunity to the people to change the existing rulers.
3. Choice and opportunity should be available to all the people on an equal basis
4. Besides political rights, some social and economical rights are offered to the citizens by the democracy.
5. Power sharing is the spirit of democracy and is necessary between government and social groups in ademocracy.
2. Ans.
1. Democratic government is a legitimate government
2. It may be slow, less efficient, not always very responsive or clean. But it is the people’s own govt.
3. There is overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world ; in countries withdemocratic regimes as well as countries without democratic regimes.
3. Ans.
1. It is necessary to understand that democracy is not simply rule by majority opinion. The majority always needs to work with the minority so that governments function to represent the general view.
2. It is also necessary that rule by majority does not become rule by majority community. In terms of religion, or race or linguistics groups. Rule by majority means that in case of every decision or in case of every election, different persons or groups may and can form a majority.
3. Democracy remains a democracy only as long as every citizen has a choice of living in majority, at some point of time.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
4. Ans. To measure a democracy on the basis of its expected outcomes we have to observe the following practices and institutions like
1. In a democracy free and fair elections should be there.
2. Open criticism and debate on major policies and legislations.
3. Citizens right to information about the functioning of government.
4. Whether the democracies are providing a fair chance to everyone, to participate in elections and decision making process.
5. Ans. Accountable: A democratic government develops mechanism for citizens to take part in decision-making process. For this free and fair elections, open debate on major policies, legislation, Right to information- such rights are given to the citizens.
Responsive: Democracy is a responsive government. It is responsive towards the needs and expectations of the citizens. It takes care and makes policies for the welfare of the citizens.
Legitimate: A democratic government is a legitimate government. It is elected by the people and people wish to be ruled by the representatives elected by them.
6. Ans. Every individual expects a lot from democracy. Democracy is expected to solve all the socio-economic, political and economic problems of the country. Democracy is expected to give equality of status to every citizen. It is expected that there would not be any type of discrimination on ground of gender, race, religion or region. The reality is that everything is expected out of democracy. Any imperfection in any such area is termed as undemocratic. It should be realized that democracy is a form of government that creates conditions which will ensure quality of citizens before the law of the country. But the citizens have to know their rights and freedom and they should try to enforce them. A democratic set up does not ensure all the right policies. Individuals have to take advantage of the good conditions created by democracy and make good policies. Thus it is not right that any information in any area is thrown on democracy.
7. Ans.
1. It promotes equality among citizens.
2. It enhances the dignity of the individuals.
3. It improves the quality of decision making
4. It provides a method to resolve conflict.
5. It allows room to correct mistake.
8. Ans.
1. In the political sphere- Right to vote, Right to contest elections.
2. In the economic sphere-Minimized Economic inequalities.
3. In the Social sphere-Equal protection to women, SCs, STs, OBCs.
9. Ans.
1. All citizens have equal role in electing representatives.
2. Parallel to the process of bringing individuals into the political arena, we find growing economic inequalities.
3. Democracy does not appear to be very successful in reducing economic inequalities.
4. The ultra-rich enjoy a highly disproportionate share of wealth and income.
10. Ans.
1. It produces a government that is accountable to the citizens, and responsive to the needs of and expectations of the citizens.
2. Democracy is based on the idea of deliberations and negations.
3. Democratic government is attentive to the needs and demands of the people.
4. A government which is able to respond to grievance faster is able to avoid confrontation and provide good governance.
Long Answers-
1. Ans. Democracy involves debates and deliberations in the parliament before making a law. The views of all the members of parliament are taken into consideration before taking the final decision. Dictatorship means decisions taken by one person or one party. Different views of other members of the government or public are not considered. Democracy means delay in the decision making process as the debates take a long time. It means that the implementation will also take time. Dictatorship means quick decisions. But those decisions are orders of the government and people are not allowed to disagree with them. Even citizens are not supposed to criticize the decisions made by the government. Democracy is better even if it takes more time in making the decisions. At least, the views of the citizens are considered and they are not ordered to just follow them. Individuals can disagree with the policies of the government and show their protest against the government.
2. Ans. In case of dignity of women, most societies across the world were historically male dominated societies. Long struggles by women have created some sensitivity today that respect to and equal treatment of women are necessary ingredients of a democratic society. That does not mean that women are actually always treated with respect. But once the democratic principle is recognized, it becomes easier for women to wage a struggle against what is now unacceptable legally and morally. Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for equal status and equal opportunity. There are instances still of caste-based inequalities and atrocities, but these lack the moral and legal foundations. Perhaps it is the recognition that makes ordinary citizens values their democratic right.
3. Ans.
1. Democracy develops a harmonious social life. Democracies accommodate various social divisions.
2. Democracies usually develop a procedure to conduct their competition. This reduces the possibility of these tensions becoming explosive or violent.
3. In democracies people learn to respect the differences and also evolve mechanism to negotiate the differences.
4. The majority always needs to work with the minority so that government functions to represent the general view.
5. Democracy has ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflict.
4. Ans. Yes, this is far of following reasons;
1. A democracy believes in equitable distribution and makes efforts to serve the poor at the root level.
2. A democracy believes in providing equal opportunity to all. Democratic governments have been supporting poor people through various schemes to uplift their economic level.
3. Poor people are being provided food and shelter at a subsidized rate and also free medicines and treatment facilities.
4. They are being insured for any unhappening’s so that their families do not get crushed.
5. They are being provided free education, reservation in educational institution and government jobs, etc.
5. Ans.
1. It has now become an accepted fact that leaders use money to win favour of the votes. This reason lessens the very sprit of democratic values.
2. There is an ever increasing tendency among the political parties to give tickets to those who are rich. The parties think that they could win not only their own seats but also help the party monetarily.
3. Now scams by leaders and governments have become a routine tale in the Indian democracy. Many of the popular leaders are facing trials for corruption charges against them.
4. It has been seen that the wards of the prominent leaders of party easily get tickets for election. The party workers keep serving for years but sometimes outsiders get tickets.
5. It has now become a traditional in many of the popular political parties that the chair is inherited.
6. Ans.
1. Decisions are made by the representatives elected by the people. These representatives represent the ideas and opinions of those voters who have elected them to take decisions on their behalf.
2. In a democracy, people want to know if a decision was taken through correct procedure, can find this out. In this way, they have some degree of control over the whole process of decision making.
3. In a democracy people have the right and mean to examine the process of decision making.
4. Sometimes important issues are put forward by the government for public debate before a decision is taken.
5. Demonstration, movement, pressure groups, etc. provide means in the hands of people to influence decision making.
7. Ans.
1. Democracy is based on the principles of equality, liberty and brotherhood. To achieve the prescribed goal the framers of our constitution adopted the aims like secularism, socialism democratic republic.
2. The framers of our constitution provided for a representative democracy in a liberal framework in order to sustain democracy.
3. In our country there are periodic elections for all levels of the government.
4. All elections are based on secret ballot and universal adult franchise.
5. Our Constitution has given complete liberty to pressure and other organized or unorganized.
8. Ans.
- Comparative analysis between democracy and dictatorship.
- It provides accountable, responsible, representative and legitimate government.
- It develops mechanism for the people’s participation in the decision making process.
- It promotes economic development. At the same time democracy has the characteristics of economic inequality and disparities.
- We can also assess its outcome on the basis of the way it accommodates the social diversities.
It also promotes dignity and freedom of the citizens
Assertion Reason Answer:
- (c) A is correct but R is wrong.
- (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
Case Study Answer:
| (i) | (c) | Right to vote. |
| (ii) | (b) | Right to information. |
| (iii) | (c) | Free and fair elections. |
| (iv) | (d) | Taken after following due processes. |
| (i) | (a) | Political equality. |
| (ii) | (a) | There is political equality for all individuals. |
| (iii) | (b) | Food, clothing, house, education and health. |
| (iv) | (a) | Their income is very less. |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science History: India and the Contemporary World-II
| Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| Chapter 3 The Making of Global World |
| Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation |
| Chapter 5 Print Culture and the Modern World |
