Modeducation are provided for CBSE RBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its compounds notes, Video Classes, Live Problem Classes, Worksheet, Test Exam Paper and Privious exam Question Solution.

NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
Bonding in Carbon: The Covalent bond, Electron dot structure, Physical properties of organic compounds, Allotropes of Carbon.
Covalent Bond: The atomic number of carbon is 6. Its electronic configuration is 2, 4. It requires, 4 electrons to achieve the inert gas electronic configuration. But carbon cannot form an ionic bond
It could gain four electrons forming C4- cation. But it would be difficult for the nucleus with six protons to hold on to ten electrons.
It could lose four electrons forming C4+ cations. But it requires a large amount of energy to remove four electrons.
Thus, carbon overcomes this problem by sharing of its valence electrons with other carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements.
The bond formed by mutual sharing of electron pairs between two atoms in a molecule is known as Covalent Bond.
Types of Covalent Bond:
- Single Covalent Bond: When a single pair of electrons are shared between two atoms in a molecule. For example; F2, Cl2, H2 etc.
- Double Covalent Bond: When two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms in a molecule. For example; O2, CO2 etc.
- Triple Covalent Bond: When three pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms in a molecule. For example; N2 etc.
Electron Dot Structure: The electron dot structures provides a picture of bonding in molecules in terms of the shared pairs of electrons and octet rule.
Formation of Hydrogen Molecule
Atomic number of Hydrogen = 1
Number of valence electrons = 1

Formation of CH4 Molecule
Atomic number of Carbon = 6 [2, 4]
Number of valence electrons = 4
Atomic number of Hydrogen = 1
Number of valence electrons = 1

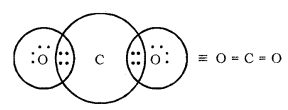
Formation of CO2 Molecule
Atomic number of Carbon = 6 [2, 4]
Number of valence electrons = 4
Atomic number of Oxygen = 8 [2, 6]
Number of valence electrons = 6
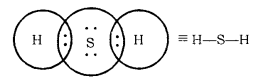
Formation of H2S Molecule
Atomic number of Sulphur = 16 [2, 8, 6]
Number of valence electrons = 6
Physical Properties of Organic Compounds
Most of the organic compounds have low boiling and melting point, due to the weak force of attraction (i.e., the inter-molecular force of attraction) between these molecules.
Most carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity, due to the absence of free electrons and free ions.
| Compounds | M.P. (K) | B.P. (K) |
| Acetic acid (CH3COOH) | 290 | 391 |
| Chloroform (CHCl3) | 209 | 334 |
| Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) | 156 | 351 |
| Methane (CH4) | 90 | 111 |
Allotropes of Carbon
Allotropy: The phenomenon in which the element exists in two or more different physical states with similar chemical properties are called Allotropy.
Carbon has Three Main Allotropes
- Diamond: In this, carbon, an atom is bonded to four other atoms of carbon forming three-dimensional structures. It is the hardest substance and an insulator. It is used for drilling rocks and cutting. It is also used for making jewellery.
- Graphite: In this, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms. It is a good conductor of electricity and used as a lubricant.
- Buckminster Fullerene: It is an allotrope of the carbon-containing cluster of 60 carbon atoms joined together to form spherical molecules. It is dark solid at room temperature.
Versatile nature of Carbon, Hydrocarbons, Isomerism, Homologous series, Functional groups, Nomenclature of functional groups.
Versatile Nature of Carbon: The existence of such a large number of organic compounds is due to the following nature of carbon,
- Catenation
- Tetravalent nature.
(i) Catenation: The self linking property of an element mainly carbon atom through covalent bonds to form long straight, branched and rings of different sizes are called Catenation.
This property is due to
- The small size of the carbon atom.
- The great strength of the carbon-carbon bond.
Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds for Class 10
What is carbon and its compounds ?
What are the types of carbon compounds?
Allotropes of Carbon
Carbon has Three Main Allotropes
Diamond
Graphite
Buckminster Fullerene
Versatile Nature of Carbon
Catenation
Tetravalent nature.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Alkenes
Alkynes
Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
Combustion
Oxidation
Oxidizing Agent
Addition Reaction
