NCERT Solutions, Question Answer and Mind Map for Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 6, “Political Parties,” is a study material package designed to help students understand the role of political parties in the Indian democracy, their formation, and their functioning.
NCERT Solutions provide detailed explanations and answers to the questions presented in the chapter. The solutions cover all the topics in the chapter, including the definition of political parties, their features, types, and functions. They also provide tips on how to answer different types of questions, including short answer, long answer, and multiple-choice questions.

The question-answer section of the chapter covers a wide range of topics, from the challenges faced by political parties in India to their role in the Indian democracy. It also includes questions on the functions of political parties, including the selection of candidates, the formation of policies, and the mobilization of voters.
The mind map provides a visual representation of the key topics covered in the chapter, allowing students to understand the connections between different concepts and ideas. The mind map covers the types of political parties, their organization, and their role in the Indian democracy.
NCERT Solutions / Notes Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 6 Political Parties with Mind Map PDF Download
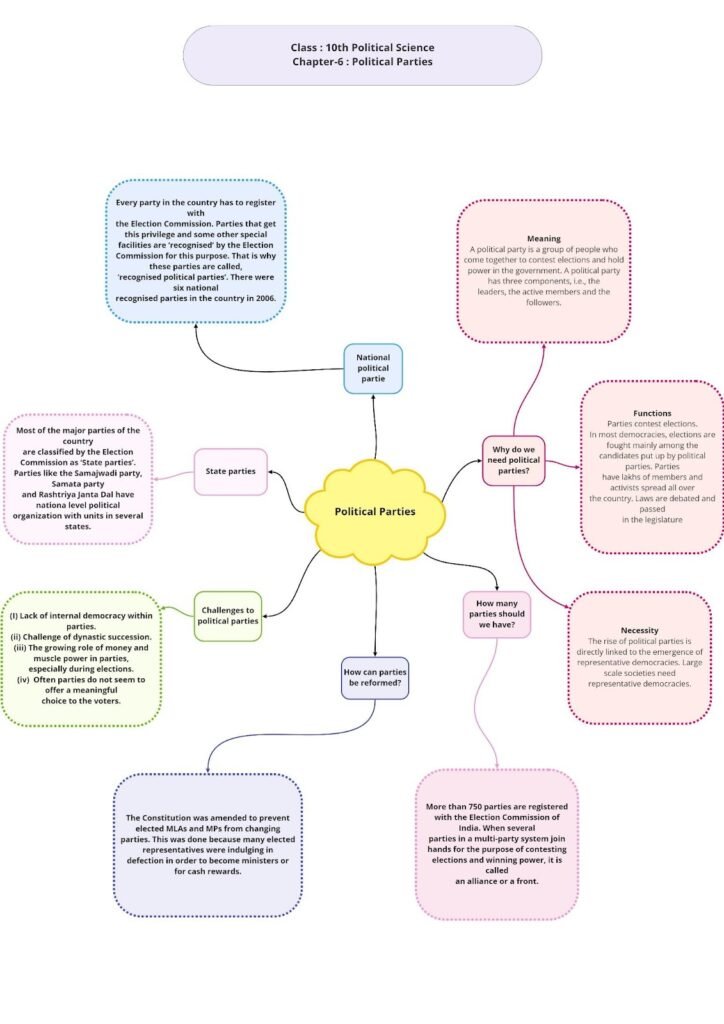
Political Parties
Meaning and Functions of a Political Party
A political party is a group of individuals who come together on a common platform. They largely have similar ideas and a common goal. Members of a political party contest elections in order to form the government at the state or at the centre. Political parties try to win the support of people by convincing them on why their policies are better than other parties. A political party has three components—leaders, active members and followers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
A political party performs many functions in a democracy.
- Political parties are required. If there are no political parties, then independent candidates would win the elections. Independent candidates may be able to manage their constituencies, but they would not be able to govern the entire country effectively because each candidate will have his/her own interests and set of beliefs.
- Each section of society chooses its representatives to represent its interests.
- Political parties also play the same role. Thus, democratic countries have political parties. The rise of political parties may be traced back to the emergence of representative democracy. As societies are large, they elect their own representatives to represent their interests. Representatives of the parties come together to form the government.
How Many Parties Should We Have?
In a democracy, any group of citizens is free to form a political party. More than 750 parties are registered with the Election Commission of India. But not all these parties are serious contenders in the elections.
Party System
The number of political parties differs from country to country.
One-party system: The formation of political parties is generally banned in countries which are ruled by dictators. Only the party to which the dictator belongs is allowed to exist. Such countries have a one-party system. For example, in China, only the Communist Party of China is allowed to contest the elections.
Two-party system: In many countries, though many parties exist, only two parties have serious chances of winning the majority of seats in the Parliament. Other parties win only a handful of seats in the national legislatures. Thus, countries with two main parties contesting the elections have a bi-party system; for example, the United Kingdom and the United States of America.
Multi-party system: When several parties exist in a country and each has the capability of forming the government either on its own or in alliance with other parties, the country has a multi-party system. India has a multi-party system. In such a system, if many political parties come together and join hands for contesting the elections and forming a government, they are known as an alliance or a front. While on one hand, the multi-party system may lead to political instability in the country, on the other, the system allows the representation of a variety of interests and public opinions.
Political Parties in India
In India, every party has to get itself registered with the Election Commission. The latter gives a symbol to the political party. A political party which has a nationwide presence and which secures at least six percent of the total votes in the Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in at least four states and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha is recognised as a national party.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
A political party which secures at least six percent of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a state and wins at least two seats is recognised as a state party.
National Parties in India
| Name of the Party | Year of Foundation | Basic Ideologies | Symbol |
| Indian National Congress | 1885 (the party has split many times) | Endorses secular principles Aims at the welfare of weaker sections and minority communities | |
| Bharatiya Janata Party | 1980 | Seeks complete integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India Believes in cultural nationalism (Hindutva) and uniform civil code for all people | |
| Bahujan Samaj Party | 1984 | Champions the cause of the dalits, adivasis and OBCs | |
| Communist Party of India-Marxist (CPI-M) | 1964 | Believes in the principles of socialism, Marxism, Leninism, secularism and democracy | |
| Communist Party of India (CPI) | 1925 | Believes in Marxism–Leninism, secularism and democracy | |
| Nationalist Congress Party | 1999 | Believes in democracy, equity, social justice and federalism |
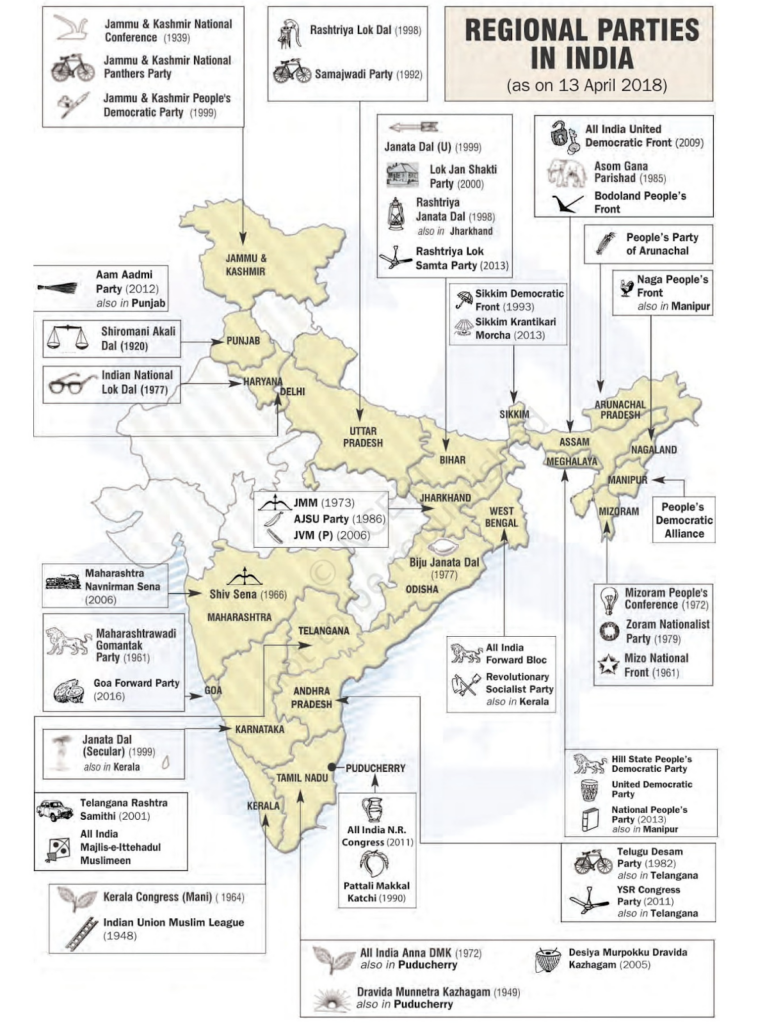
State Parties in India
List of major state parties in India:
- Samajwadi Party (largely present in Uttar Pradesh)
- Rashtriya Janata Dal (Bihar)
- Trinamool Congress (West Bengal)
- Biju Janata Dal (Odisha)
- Sikkim Democratic Front (Sikkim)
- National Conference (Jammu and Kashmir)
- Peoples Democratic Party (Jammu and Kashmir)
- DMK (Tamil Nadu)
- AIADMK (Tamil Nadu)
(See the map on the next pa g e for details of these parties).
Challenges to Political Parties
Main challenges faced by political parties in India are
- Lack of internal democracy: There is a lack of internal democracy within the political parties. Most of the parties do not keep membership registers and do not conduct elections regularly. Dynastic succession does not allow a deserving candidate to rise to a position of leadership.
- Money and muscle power: Because the main aim of the political party is to win an election, many candidates who could raise a lot of money are nominated. Influential and wealthy party members exercise greater control over party politics. Parties have also become corrupt.
- Lack of meaningful choice: Most of the parties do not offer meaningful choices to the people. Fundamental differences among the parties have reduced.
How Can Parties be Reformed?
Political parties can be reformed in the following ways:
- A law to prevent the defection of a party member in hope of money and power was passed in the Parliament. It is necessary to strictly follow this law.
- An order has been passed requiring candidates contesting the elections to declare their assets and criminal charges pending against them. This was done to reduce the influence of money and criminals in parties. This law also needs to be strictly followed.
- Every political party should regularly hold organisational elections and file income tax returns.
- It should be made mandatory for political parties to give at least one-third of the party’s tickets to women candidates.
- Elections should be funded by the state.
Many suggestions have not been accepted by political parties; thus, it is important for the public to organise protests and rallies to demand the passing of laws to this effect. The functioning of political parties can be further improved if the people who support these changes join the parties.
Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 6 Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions-
Question 1. The number of parties registered with the Election Commission of India is:
(a) 550
(b) 650
(c) 750
(d) 850
Question 2. One-party system refers to:
(a) When only two parties are allowed to control and run the government
(b) When three parties are allowed to control and run the government
(c) When one party is allowed to control and run the government
(d) None of the above
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Question 3. In China, the only one party that is allowed to rule is the:
(а) Congress Party
(b) BJP
(c) Socialist Party
(d) Communist Party
Question 4. Any democratic system must allow at least:
(a) One party to compete in elections
(b) Two parties to compete in elections
(c) Three parties to compete in elections
(d) Several parties to compete in election
Question 5. Two party system exists in:
(a) USA and China
(b) UK and India
(c) USA and UK
(d) India and China
Question 6. In India, there is a:
(а) One-party system
(b) Two-party system
(c) Multi-party system
(d) None of the above
Question 7. In India, in 2004 there was an alliance in Parliamentary elections between the:
(a) National Democratic Alliance, the United Progressive Alliance and the Left-Front
(b) National Democratic Alliance, the BJP and Akali Dal
(c) National Democratic Alliance, BJP and Samajwadi Party
(d ) United Progressive Alliance, the Left Front and the BJP
Question 8. National parties are those parties which have their units :
(a) In some states
(b) In various states
(c) In the capital city
(d) None of the above
Question 9. Every party in the country has to register with the:
(a) Government
(b) Local government
(c) Election Commission
(d) MCD
Question 10. A party is recognised as a national party if it secures at least six percent of the total votes in Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four states and:
(a) Wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha
(b) Wins at least three seats in the Lok Sabha
(c) Wins at least two seats in the Lok Sabha
(d) Wins at least one seat in the Lok Sabha
Question 11. In 2006, the number of recognised parties in the country were:
(a) Three
(b) Four
(c) Five
(d) Six
Question 12. The challenges to political parties are:
(a) Internal democracy
(b) Money and muscle power
(c) Meaningful choice
(d) All of the above
Question 13. In a democracy, the final decision is made by:
(а) The government
(b) The President
(c) Leaders who represent political parties
(d) Leaders who do not represent political parties
Question 14. MPs and MLAs have to accept whatever the:
(a) Party leaders decide
(b) Party decides
(c) Government decides
(d) Election Commission decides
Question 15. The Election Commission passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organisational elections and:
(а) Pay their house tax
(b) Pay their house rent
(c) Pay their expenditure
(d) File their income tax returns
Very Short Questions-
- Who exercise the real power in the Democracy?
- What is Partisan?
- What are bye elections?
- Name the oldest recognized Political Party of India?
- Which Political party draws inspiration from the Ideas and teachings of Mahatma Gandhi, J Phule and Sahu Maharaj?
- Name the National Political Party who is against the conversion of religion?
- Name the political Party who wants full territorial and political integration of Jammu and Kashmir with India?
- What are leftist Parties?
- When was CPI-M founded?
- What is Multi- Party system?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Short Questions-
1. What are the main functions of a political party?
2. What are the challenges between political parties in India?
3. Mention the features of Congress party in India?
4. Name six National Political Parties of India along with their symbols.
5. Explain the requirements fulfilled by a political party to become a national political party.
6. Write down the name of regional political party dominant in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and West Bengal.
7. Why are symbols allotted to political parties by the election commission of India? Give reason?
8. What is a political party? What are the components of a political party?
9. Explain the constitutional measures to counter challenges faced by political parties.
10. Write down the parameters laid down by the Election Commission of India to recognize the State Political Parties and National Political Parties.
Long Questions-
1. Explain elements of four basic elements of Political Party.
2. “Increase in the number of states or regional parties strengthen democracy in India”. Justify the state with suitable examples.
3. State the various functions political parties perform in a democracy.
4. The political scene is the mass of many parties. How do politicians manage these coalitions? Give your opinion.
5. Suppose, you are going to form a political party. What ideology would you like to keep in mind? Explain.
6. How would you explain the situation without political parties in country?
7. What is Multi-Party system? Discuss the merits and demerits of multi-party system.
8. Explain the meaning of a Political Party. Mention its components. Name any two recognized national parties in India.
Assertion Reason Questions:
- Directions: – In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true but R is false
- A is false bur R is true
Assertion (A): If the budget presented to the Rajya Sabha is not passed within the
stipulated period, the budget proposals are not affected.
Reason (R): In financial matters, the Lok Sabha is more powerful than the Rajya Sabha.
- Directions: – In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
- Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
- Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A
- A is true but R is false
- A is false bur R is true
Assertion (A): In India political parties which formed the government represent the
majority of seats secured in the elections to the House of the People at the Centre and the Legislative Assemblies in the States but not the Majority of votes.
Reason (R): The elections based on the majority vote system decided the result on the basis of relative majority of votes secured.
Case Study Questions:
- We can understand the necessity of political parties by imagining a situation without parties. Every candidate in the elections will be independent. So, no one will be able to make any promises to the people about any major policy changes. The government may be formed, but its utility will remain ever uncertain. Elected representatives will be accountable to their locality. But no one will be responsible for how the country will be run. We can also think about it by looking at the non-party based elections to the Panchayat in many states. Although the parties do not contest formally, it is generally noticed that the village gets split into more than one faction, each of which puts up a panel of its candidates. Thus, it is exactly what the party does. That is the reason we find political parties in almost all countries of the world whether these countries are big or small, old or new, developed or developing.
The rise of political parties is directly linked to the emergence of representative democracies. As we have seen, large societies need representatives of democracy. As societies became large and complex, they also need some agency to gather different views on various issues and to present these to the government.
- Why is the existence of a Political Party necessary for democracy?
(a) Political Parties help to develop a public opinion.
(b) No independent candidate can make any promise to the people.
(c) Independent elected representatives are only responsible for their own constituency.
(d) Political Parties helps to inculcate insecurity among the people
- ‘Political Faction’ means a group of individuals within a political party that share a ……………. Identify.
(a) Balanced view
(b) Common political purpose
(c) Regional and communal diversities
(d) Ideal political structure
- Consider the following statements about political parties and choose the correct option.
I. Political Parties are a necessary condition for democracy.
II. Political Parties help the government to make policies.
III. Political Parties justify or oppose the representative governments.
Options:
(a) Only I
(b) Both I and II
(c) Both II and III
(d) All of the above
- Which of the following describes representative democracy?
(a) It is not a common form of democracy in the modern age.
(b) It involves direct participation.
(c) It involves indirect participation through elected representatives.
(d) It was the most prevalent form of democracy in the Colonial Era
- Why does a large society need representative democracies?
(a) To form a responsible government.
(b) To form an ideal form of government.
(c) To gather public opinions.
(d) To resolve issues of minority communities
MCQ Answers-
- Answer: (c) 750
- Answer: (c) When one party is allowed to control and run the government
- Answer: (d) Communist Party
- Answer: (b) Two parties to compete in elections
- Answer: (c) USA and UK
- Answer: (c) Multi-party system
- Answer: (a) National Democratic Alliance, the United Progressive Alliance and the Left-Front
- Answer: (b) In various states
- Answer: (c) Election Commission
- Answer: (a) Wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha
- Answer: (d) Six
- Answer: (d) All of the above
- Answer: (c) Leaders who represent political parties
- Answer: (a) Party leaders decide
- Answer: (d) File their income tax returns
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Very Short Answers-
- Ans. Citizens of the country
- Ans. A person who is strongly committed to a party, group or faction. Partisanship is marked by a tendency to take a side and inability to take a balanced view on an issue.
- Ans. Elections which are held to fill a vacancy caused by the death of any elected member or of any other reason, for example defection.
- Ans. Indian National Congress
- Ans. Bahujan Samaj Party.
- Ans. Bharatiya Janta Party
- Ans. Bharatiya Janta Party
- Ans. Left often refers to those who are in favor of the poor, downtrodden section and support government policies for the benefit of these sections.
- Ans. . Communist party of India-Marxist was founded in 1964.
- Ans. If several parties compete for power, and more than two parties have reasonable chances of coming to power either on their own strength or in alliance with others, we call it a multi-party system.
Short Answers-
1. Ans.
1. To contest election
2. Forming policies and programmes
3. Making laws
4. Parties form and fun govt.
5. To play an active role of opposition
6. Shaping public opinion
7. Access to govt. machinery and welfare schemes
2. Ans. Following points can be given with explanation as the challenges of political parties in India—
1. Lack of internal democracy
2. Lack of transparency
3. Use of money and muscle power
4. Not providing meaningful choice to the voter
3. Ans.
1. Congress party was founded in 1885 and has experiences many splits.
2. It was ruling party at the centre till 1977 and then in 1880-89, 2000 to till date
3. This party supports secularism and welfare of weaker sections and minorities.
4. It supports new economic reforms but with a human face.
5. It emerged as the largest party with 145 seats in the Lok Sabha elections in 2004.
6. It currently leads the ruling united progressive alliance (UPA) coalition govt. at the centre.
4. Ans.
1. Indian National Congress Hand
2. Bharatiya Janta Party Lotus
3. Bahujan Samaj Party Elephant
4. Communist Party of India-(Marxist) Sickle, Hammer and Star
5. Communist Party of India Sickle and Wheat
6.Nationalist Congress Party Clock
5. Ans.
1. The party has to secure at least six percent of the total votes in the Lok Sabha elections.
2. Six percent of the total votes in the state Assembly elections and win at least four seats in the Lok Sabha protected against the marketing of goods and delivery of services that are hazardous to life and property.
6. Ans.
1. Andhra Pradesh- Telgu Desam Party (1982), Telangana Rashtra Sammiti (2001)
2. Karnataka- Janata Dal (secular)1999
3. West Bengal- Forward Bloc (1940), Revolutionary Socialist Party (1940), Trinamool Congress (1977).
7. Ans.
1. For the recognition of the political parties the symbols are required.
2. It means party is large and established.
3. Only the official candidates of the political party can use it.
4. Voters can caste their vote easily.
5. One can easily recognize the party is either a national or regional party.
8. Ans. A political party is a association of people who come together to contest elections and keen to hold power in the government. Political parties put forward different policies and programs and the voters choose for them. Parties play a decisive role in making laws for a country. Following are the components
1. The Leaders.
2. The Active Members.
3. The followers
9. Ans.
1. The constitution was amended to prevent elected MLAs and MPs from changing parties. This is called anti defection law.
2. The Supreme Court made it mandatory for every candidate to file an affidavit giving details of his property and criminal cases pending against him.
3. The Election Commission made it necessary for political parties to hold elections and file their Income tax Returns.
10. Ans.
1. Every party in the country has to register with the Election Commission.
2. In a state party the party members aim to highlight the regional interest. On the other hand, a national party gives due importance to national interests.
3. State party: A party that secures at least six percent of the total votes in the election to the Legislative assembly of a state and wins at least two seats is recognized as a state party.
4. National party: A party secure at least six percent of the total votes in the Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four states and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha is recognized as a national party.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Long Answers-
1. Ans.
1. National and Regional Interest: Political parties have national and regional interests. Their main aim is to promote national interests.
2. Constitutional Interest: A political party must follow the constitutional means in a peaceful manner in order to capture political power.
3. Organisation: The member of political party with concern interest forms a organization that is political party.
4. Common Aim: Its members must have a similar and unanimous opinion regarding public matters and issues
2. Ans. India is federal country and the powers of the Government are divided into different levels. Decentralization of power means expansion of democracy. If the number of state or regional parties is increasing it means the people of our country are becoming more aware and they are not happy with the working of existing political parties. In these days regional parties have a say in political policies as they win elections in their states. The national political parties have to take help of the regional parties to win the elections or to form the government. The rise of collision governments broadened the concept of popular participation. It also strengthen the federal system of the democracy.
3. Ans.
1. Political parties contest elections. In most democracies, elections are fought mainly among the candidates put up by the parties. Parties select their candidates in different ways.
2. Parties’ forward different policies and programs and voters choose them from. Each of us may have different opinions and views on what policies are suitable for society. A government is expected to base its policies on the line taken by the Ruling Party.
3. Parties play a decisive role in making laws foe a country. Laws are debated and passed in the legislature. But most of the members of legislature are the members of political parties.
4. Parties form and run the Governments. As we noted last year, the big policy decision are taken by political executive that comes from the political parties.
5. Those parties that lose in the elections play the role of opposition of the parties in power, by voicing different views and criticizing government for its failure or wrong policies.
4. Ans. It is true that presently political scene is dominated by many political parties. Many National and Regional Political parties are working at local level and regional level. If we take this concept in positive sense we will find out the following conclusions
1. Many political parties give chance of popular participation
2. Many political parties give choice to the people
3. Give a chance for equal representation to everyone
4. His system has strengthens the federal system and democracy of the country.
5. The politicians do manage these coalitions by giving proportional representation to all emerging political parties and their members
5. Ans.
1. Aim and objective: Secularism, patriotism, no place for casteism, welfare of women. Promotion of weaker sections and minorities and above all economic development would be the basis of our country.
2. Internal Democracy: We would promote internal democracy. There would be routine organizational elections for various party posts.
3. No favoritism: In many political parties the most important posts is held by the member of a particular family and it takes inheritable nature. This neglects the rights of other deserving leaders and damage democratic values. Our party would choose the leaders for top post through internal elections.
4. No role of money and Muscle power: There would be a place for money and muscle power to win elections.
5.People’s participation: We would include those policies in our manifesto that would encourage people’s participation in the political system.
6. Ans.
1. We can understand the necessity of political parties by imagining a situation without parties.
2. The every candidate in the elections will be independent. So no one will be able to make any promise to the people about any major policy changes.
3. The government will be formed but its utility will remain ever uncertain.
4. Elected representatives will be responsible only to their constituency and not for the entire country.
5. But no one will be responsible for how the country run.
6. Elections without political parties will also be responsible for the disintegration of the country.
7. Ans. Multi-Party system: If several parties compete for power and more than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming into power, either own strength or in alliance with other, we call it multi-party system.
Merits:
1. This system allows a variety of interests and opinions.
2. People can take a choice between several candidates.
Demerits:
1. No one party is likely to gain power alone. Therefore, it is difficult in formation of government.
2. It leads to political instability.
8. Ans. A political party is a group of people that come together to contest elections and hold power in the government. They agree on some policies and programs for the society with a view to promote the collective good. Since there can be different views on what is good for all, parties try to persuade people as to why their policies are better than others. They seek to implement these policies by winning popular through elections.
Components of Political Party:
1. The leaders.
2. The active members.
3. The followers.
Two recognized national parties:
1. Bhatatiya Janta party
2. Indian National Congress
Assertion Reason Answer:
- (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
- (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
Case study Answer:
- i (a) Political Parties help to develop a public opinion.
ii (b) Common political purpose
iii (d) All of the above
iv (c) It involves indirect participation through elected representatives.
v (a) To form a responsible government.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science History: India and the Contemporary World-II
| Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| Chapter 3 The Making of Global World |
| Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation |
| Chapter 5 Print Culture and the Modern World |
