NCERT Solutions, Question Answer and Mind Map for Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 8, “Challenges to Democracy,” is a study material package designed to help students understand the challenges faced by democratic governments and the ways to overcome them.
The NCERT Solutions provide detailed explanations and answers to the questions presented in the chapter. The solutions cover all the topics in the chapter, including the meaning and importance of democracy, the challenges faced by democratic governments, and the ways to overcome these challenges. They also provide tips on how to answer different types of questions, including short answer, long answer, and multiple-choice questions.

The question-answer section of the chapter covers a wide range of topics, from the meaning and importance of democracy to the various challenges faced by democratic governments, including corruption, communalism, and poverty. It also includes questions on the ways to overcome these challenges, including the role of civil society and media in strengthening democracy.
The mind map provides a visual representation of the key topics covered in the chapter, allowing students to understand the connections between different concepts and ideas. The mind map covers the meaning and importance of democracy, the challenges faced by democratic governments, and the ways to overcome these challenges.
NCERT Solutions / Notes Class 10 Social Studies Civics Chapter 8 Challenges to Democracy With Mind Map PDF Download
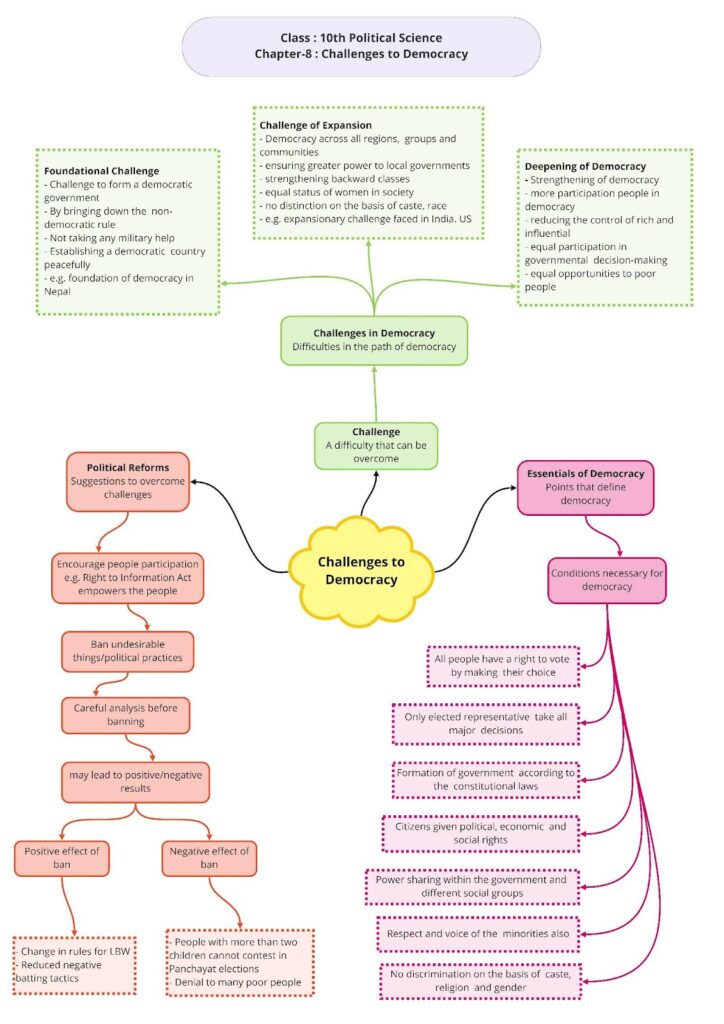
Challenges to Democracy
Democracy and Challenges
Democracy is considered the best form of government. However, it faces many challenges. On a global level, democracy faces three challenges.
- Foundational Challenge: This challenge is faced by the people of non-democratic countries. This includes throwing off the dictatorial regime, to not allow the military to assume control and to establish a democratic and a sovereign state. Countries such as Syria and Iraq face this kind of challenge.
- Challenge of Expansion: Several countries where democracy is already established face the challenge of expansion. Greater representation to local bodies and inclusion of women and minority groups in politics are challenges faced by democratic countries. Countries such as India and the USA face this kind of challenge.
- Challenge of Deepening of Democracy: This challenge is faced by almost all democratic countries. The main challenges for the government are to strengthen democratic institutions and practices of democracy (e.g. to control the influence of rich and powerful people in deciding laws and policies).
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Political Reforms
All proposals forwarded to overcome various challenges faced by democratic countries are known as ‘democracy reforms’ or ‘political reforms’. Certain points need to be kept in mind while promulgating democracy reforms in the country. These are
- Laws to curb bad or corrupt practices in the country are not always easy to promulgate. They may help the democratic spirit of the country to strengthen but cannot completely overcome the challenges posed to democracy. Any democratic reforms should be carried out mainly by political activists, movements, political parties and conscious citizens.
- Before implementing democratic reforms, it is important to carefully study the impact of such reforms on society as a whole. Sometimes, the results of such reforms may be counterproductive. For example, many states have banned men and women who have more than two children from contesting panchayat elections. This has actually robbed the people of their right to contest elections. However, some laws or Acts may prove beneficial for democracy in the long run. For example, the Right to Information Act.
- Democratic reforms should not only be brought about to strengthen governmental institutions but also to increase and improve the quality of political participation by citizens of the country.
Redefining Democracy
Democracy is the form of government in which people elect their own representatives. Apart from this, democracy has some more important features. These are
- All major decisions are taken by leaders elected by the people of the country.
- A fair opportunity should be provided to the people to change the current government.
- The above opportunity should be available to all people on an equal basis.
- Right to vote and the principle of one vote having one value are important aspects of democracy.
- Holding of free and fair elections is an important condition required for the successful working of a democracy. Power sharing is an integral part of democracy.
- A majority community should not dominate the minorities. The voice of the latter should be heard and respected by the majority.
- It is important to eliminate gender, social, religious and caste differences in society. Here we have summarised the points that you have learned in democratic government and politics.
- You have learned the democratic rights at length and understood that these rights are not limited to the right to vote, stand in elections and form political organisations. Also, you have read about some social and economic rights that democracy should offer to its citizens.
- You get to know that power-sharing is the spirit of democracy and how power-sharing between governments and social groups is necessary in a democracy. You saw how democracy cannot be the brute rule of the majority and how a respect for the minority voice is necessary for democracy.
- You have learned how eliminating discrimination based on caste, religion and gender is important in a democracy. Finally, in this chapter, you get to know about the outcomes of democracy.
Important Questions
Multiple Choice questions-
Question 1. Which one of the following laws was enacted by the Government of India in October 2005?
(a) The Right to Property Act
(b) The Right to Education Act
(c) The Consumer Protection Act
(d) The Right to Information Act
Question 2. Which one of the following is a foundational challenge of democracy?
(a) Empowering women
(b) Keeping military away from controlling government
(c) Ensuring greater power to local governments
(d) Empowering minority groups.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Question 3. Which one of the following is an indicator of deepening of democracy?
(a) Installation of democratic government
(b) Keeping military away from controlling government
(c) Strengthening of the practices of democracy
(d) Inclusion of women in party politics
Question 4. Which legal act is the best to empower people to carry out democratic reforms?
(a) The Right to Information Act
(b) The Right to freedom
(c) The Right to education
(d) The Right to move freely
Question 5. Every established democracy faces
(a) challenge of expansion
(b) challenge of deepening of democracy
(c) foundational challenge
(d) dictatorship
Question 6. Looking at the expanded definition, which one of the following statements is not correct about democracy?
(a) The rulers elected by the people must take all the major decisions.
(b) Elections must offer a fair choice to the people to change the current rulers.
(c) The choice should be available to all people on an equal basis.
(d) To exercise this choice government must not be limited by basic rules of the Constitution and citizens’ rights.
Question 7. In Nepal, Constituent Assembly about to be elected, unrest in Terai areas, Maoists have not surrendered arms.
(a) Foundational challenge
(b) Challenge of expansion
(c) Deepening of democracy
Question 8. In Belgium, one round of constitutional change takes place, but the Dutch speakers, not satisfied, want more autonomy.
(a) Foundational challenge
(b) Challenge of expansion
(c) Deepening of democracy
Question 9. Democracy does not stand for:
(a) Democratic Right
(b) Elections
(c) Violence
(d) Accommodation of diversity
Question 10. Which one of the following situations represents the success of democracy?
(a) US as the only Super power disregards the UN and takes unilateral action.
(b) General Pinochet government defeated, but army is still under control of many institutions.
(c) The King of Nepal Birendra accepted constitutional Monarchy.
(d) Integration of French speaking and Dutch speaking people in Belgium.
Question 11. Which one of the following is not true regarding ‘Democratic Reforms’?
(a) Legal measures can sometimes prove to be counter-productive.
(b) The media should play an active role.
(c) Legal measures always help in reforming politics.
(d) Political empowerment and participation of citizens can help.
Question 12. What is the tempting way of reforming politics?
(a) Legal ways
(b) Illegal ways
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Question 13. How many parts of the globe is not under democratic government?
(a) One-sixth
(b) One-fourth
(c) One-third
(d) None of the Above
Question 14. Which one of the following countries is facing the challenge of expansion of democracy?
(a) India
(b) US
(c) Sri Lanka
(d) All of the above
Question 15. What is not true regarding a challenge?
(a) Any sort of problem or difficulty is called a challenge.
(b) A challenge is a difficulty which is significant and which can be overcome.
(c) A challenge is a difficulty that carries within it an opportunity for progress.
(d) Once we overcome a challenge, we go up to a higher level than before.
Very Short Questions-
- Which country was facing the ethnic tension between Serbs and Albanians?
- Name the country where Suu kyi spend more than 15 year in house arrest.
- How much part of the globe is still not under the democratic governments?
- Name the person who become Prime Minister after Bolivia’s water war and was a big supporter of water struggle.
- “Women are not allowed to take part in public activities, no freedom of religion for minorities” This statement shows which type of challenge to democracy?
- Which reform proposal can reduce the rise of money power in politics?
- What are the suggestions about overcoming various challenges to democracy called?
- Give any one example of a challenge of expansion that democracy faces.
- Write one challenge of expansion faced by all established democracies.
- Strengthening of institutions to increase people’s participation and control is an example of which type of challenge of democracy?
Short Questions-
1. How is the challenge of deepening of democracy faced by every democracy?
2. Enumerate there challenges which democracies in the world face today.
3. What does fundamental challenge to democracy mean? Which two aspects are included in this challenge?
4. “Challenge of expansion is a very common which is mostly faced by established democracies.” Comment.
5. Explain any three measures to deepen democracy in a country?
6. “Laws that give political actors incentives to do good things have more chances of working”. Explain.
7. What are the things included in the challenges of expansion to modern democracy?
8. “At least one fourth of the globe is still not under democratic government”. Explain the statement in contest of the challenge of democracy.
9. How can democratic reforms are brought about. Explain any three ways.
10. Read the case and context of the following countries and write in your word the description of the challenges for the democracy in the given situation.
Chile: General Pinochet’s government defeated, but military still in control of many institutions.
Poland: After the first success of solidarity, the government imposed martial law and banned solidarity
Long Questions-
1. How would you explain that an ordinary citizen can play a very constructive role in the depening of democracy?
2. What is the nature and scope of Democracy in the modern world?
3. Can you explain any five challenges and problems faced by Indian Democracy?
4. Describe the expanded scope of democracy in the modern world.
5. Do you have any source to get the information about the working of government? Explain.
6. What is foundational Challenge? Explain with the suitable example of those countries who are trying to establish a democratic set up.
7. Suggest some reform proposals to overcome the challenge of Political Funding.
8. Describe the expanded form of democracy in the modern world?
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
Assertion Reason Question:
- Directions: In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false bur R is true
Assertion (A): At least one fourth of the globe is still not under democratic government.
Reason (R): Because the challenge for democracy in these parts of the world is very stark.
- Directions: In the following questions, the Assertions (A) and Reason(s) (R) have been put forward. Read both statements carefully and choose the correct answer from the below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false bur R is true
Assertion (A): Power sharing is the spirit of democracy.
Reason (R): As the rights of the people are not limited to the right to vote, stand in elections and form political organizations.
MCQ Answers-
- Answer: (d) The Right to Information Act
- Answer: (b) Keeping military away from controlling government
- Answer: (c) Strengthening of the practices of democracy
- Answer: (a) The Right to Information Act
- Answer: (a) challenge of expansion
- Answer: (d) To exercise this choice government must not be limited by basic rules of the constitution and citizens’ rights.
- Answer: (a) Foundational challenge
- Answer: (b) Challenge of expansion
- Answer: (c) Violence
- Answer: (d) Integration of French speaking and Dutch speaking people in Belgium.
- Answer: (c) Legal measures always help in reforming politics.
- Answer: (a) Legal ways
- Answer: (b) One-fourth
- Answer: (d) All of the above
- Answer: (a) Any sort of problem or difficulty is called a challenge.
Very Short Answers –
- Ans. Yugoslavia
- Ans. Myanmar
- Ans. At least one fourth of the globe is still not under democratic government.
- Ans. Morales
- Ans. Deepening of democracy
- Ans. There should be state funding of elections
- Ans. Political Reform
- Ans. Applying the basic principles of democratic government across all regions, social groups and various institutions.
- Ans. Ensuring greater power to local governments.
- Ans. Challenges of deepening of democracy
Short Answers –
1. Ans.
1. This involves string tuning of the institutions and practices of democracy.
2. This should happen in such a way that people can realize their expectations of democracy.
3. In general terms, it usually means string tuning those institutions that help people’s participation and control.
4. This requires an attempt to bring down the control and influence of the rich and powerful people in making governmental decisions.
2. Ans.
1. Fundamental challenge — Those countries which do not have democratic form of govt. face the fundamental challenge of establishing democracy in the country.
2. Challenge of Expansion.—Countries having democratic setup face the challenge of expansion.
3. Deepening of Democracy – This challenge is faced by almost all the democracies. This involves strengthening of the institutions and practices of democracies.
3. Ans. Those countries which do not have democratic form of govt. face the foundational challenge of establishing democracy in the country. This involves bringing down the existing non-democratic govt. to keep the military away from capturing power and establishing a sovereign democratic state.
4. Ans. Challenge of expansion is a very common which is mostly faced by established democracies. Even this challenge is faced by the United States of America, the most stable democracy of the world. This challenge believes in the expansion of political and democratic rights among the citizens. This challenge includes:
1. Extension of democratic power to local governments.
2. Expansion of federal principals to the federal units.
3. Political empowerment to women and minorities
5. Ans.
1. The most important step to deepening the democracy in a country is spreading the education among the citizens of the country. The literate population is the most important human capital of the country. Education brings qualitative changes in the citizens and enables them to use better tools and knowledge for the better governance.
2. Press should have full freedom to form the public opinion. Press makes the public aware about the happenings in the country and keeps them informed. So people should know the strength of the press.
3. For the deepening of democracy each and every person should be aware about his/her fundamental rights. He should be political aware. Government should take some steps to be spread awareness about their fundamental rights
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
6. Ans. Yes, I am agreeing with this statement. Any legal change must carefully look at what results it will have on politics. Sometimes the results may be counter-productive. For example, many states have banned people who have more than two children from contesting panchayat elections. This has resulted in denial of democratic opportunity to many poor and women, which was not instead. Generally, laws that seek to ban something are not very successful in politics. Laws that give political actors incentives to do good things have more chances of working. The best laws are those which empower people to carry out democratic reforms.
7. Ans.
1. Applying the basic principles of democratic government across all over the regions.
2. Different social groups and various institutions and ensuring greater power to local governments.
3. Extension of federal principle to all the units of the federation, inclusion of women and minority groups.
8. Ans. In about one fourth of the globe there are challenges for democracy and countries are still not under democratic government.
1. The challenges for democracy in these parts of the world are very stark.
2. These countries face foundational challenge of making the transition to democracy so as to institute democratic government.
3. This involves bringing down existing non-democratic regime, keeping military away and establishing sovereign and functional state.
9. Ans.
1. The main focus of political reforms can be by strengthening democratic practices.
2. By increasing and improving the quality of political participation by ordinary citizens. It is very difficult to implement the reforms through legal ways.
3. The challenges to democracy require some forms of reforms.
10. Ans. Chile: According to the description this country is facing the challenge of Expansion. Establishing civilian control over all governmental institution, holding the first party elections, recalling all political leaders from exile.
Poland: Country is facing foundational challenge.
- To bring down the existing non democratic regime.
- To remove martial law.
Government freed to form Associations
Long Answers –
1. Ans.
1. A democracy is a type of government and it cannot function in the absence of enlightened and aware citizens because they are the pillars of democracy.
2. Well informed citizens maintain a balance between government and social issues.
3. Well informed citizens form a healthy public opinion which puts a check on irresponsible behavior of the government.
4. Socially responsible citizens also help in the regulation of social reforms and put a check on the rash and unsocial conduct of political parties and public also.
5. The strength of democracy lies in respecting its citizens and in creating atmosphere of fair and frank interaction of thoughts, approaches and perspectives for solving collective problems and building a polity of free and equal beings.
2. Ans.
1. There is a due respect for democracy in the modern world. It is a better form of government as comparison to its alternatives.
2. It may be slow and less efficient but it is an accountable, legitimate and responsible form of government.
3. There is an overwhelming support for the Democracies all over the world because Democratic Governments are people’s own Government.
4. Countries of the modern world which are ruled by dictators and military rulers are trying to establish democracies in their own countries.
5. The hide and seek of democracy in Pakistan shows that the natives are expecting democracy in the country.
6. The establishment of democracy in Nepal also shows the dominant position of democracy in the world.
3. Ans.
1. Challenge of expansion: Indian democracy is facing the challenge of expansion. This challenge of Indian democracy involves he practical aspects like-ensuring grater power to local governments, extension of federal principals to all the units of the federation, inclusion of women and minority groups.
2. Problem of Casteism: Casteism playing a major role in the Indian politics. There are many caste based pressure groups and interest groups. All these influence those who are in power. Casteism is also harmful for the unity of the country.
3. Problem of Communalism: Communalism has also is negative implication in Indian Politics. It leads to intolerance, suspicion and fear towards members of the other communities. Besides this there are various types of communal violence in the society.
4. Problem of Corruption: This problem of Indian democracy is related to the criminal record and personal possession of politicians. Corruption is an obstacle in the development of Indian economy.
5. Problem of Criminalization: Money and muscle power is used during elections. Here is a lack of electoral ethics and insufficient representation of various sections of society like minorities and women.
4. Ans.
1. There is one respect in which democratic government is certainly better than its alternatives: Democratic government is a legitimate government. But it may be slow less efficient, not always very responsive or clean.
2. A democratic government is people’s people own government. That is why; there is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world.
3. As the accompanying evidences from South Asia shows, the support exists in countries with democratic regimes as well as countries without democratic regimes.
4. People wish to be ruled by representatives elected by them. They also believe that democracy is suitable for their country.
5. Democracy’s ability to generate its own support is itself an outcome that cannot be ignored.
5. Ans. RTI is a source to get the information about the working of government in India. The Right to information is a good example of a law that empowers the people to find out what is happening in government.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
1. The Right to Information Act was implemented on 12 October 2005.
2. This act enabled people to know about every detail of any programs from the levels of planning to implementations. By this they can know lapses, misappropriation, etc. if any officials and file a complaint and corruption and impose strict penalties.
3. This law helps to know who has taken the decision, was the decision taken as per the established norms and procedures. So the executive have to think twice before taking any biased decisions.
6. Ans.
1. The challenge for democracy in these parts of the world is very stark. These countries face the foundational challenge of making the transaction to democracy and then instituting democracy government. This involves bringing down the existing non-democratic regime, keeping military away from controlling government and establishing a sovereign and functional state.
2. Example: Iraq is facing the foundational challenge. Widespread sectarian violence as the new government fails to establish its authority.
7. Ans.
1.Role of money in elections in India has been increasing for the last few years. It is necessary to curb the role of money to make democracy more successful.
2. Auditing of account of the political parties and state funding are good reform proposals. These reforms will bring transparency in the finances of the political parties.
3. State funding will reduce the expenditure on elections. Role of money will be less and poor people may also be able to contest elections.
4. Election Commission should work honestly while checking the income taxes filed by the political parties.
8. Ans.
1. A democratic Government is people’s own Government. In Democracy rights are not limited to the right to vote, it also provides some social rights and economic rights.
2. It is accountable, responsive and legitimate government. It give respect to the voice of minority groups.
3. People wish to be ruled by representatives elected by them. They also believe that democracy is suitable for their country.
4. Democracy’s ability to generate its own support is itself an outcome that cannot be ignored.
Assertion Reason Answer:
- (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6th SSt
- Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science History: India and the Contemporary World-II
| Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe |
| Chapter 2 Nationalism in India |
| Chapter 3 The Making of Global World |
| Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation |
| Chapter 5 Print Culture and the Modern World |
